Explore 3D fingerprinting
Fingerprint science is driven by the hunt to capture increasingly reliable, higher quality fingerprint images. Until recently, even the highest resolution fingerprinting was restricted to two dimensions. Imagine what we can achieve when we can access to the full topography—length, width, and depth—of a fingerprint.
Forensic fingerprinting with 3D imaging
- Improved matching
- High quality imaging
- Spoof resistance
- 3D minutiae matching
- 3D curvature matching
- True core point detection
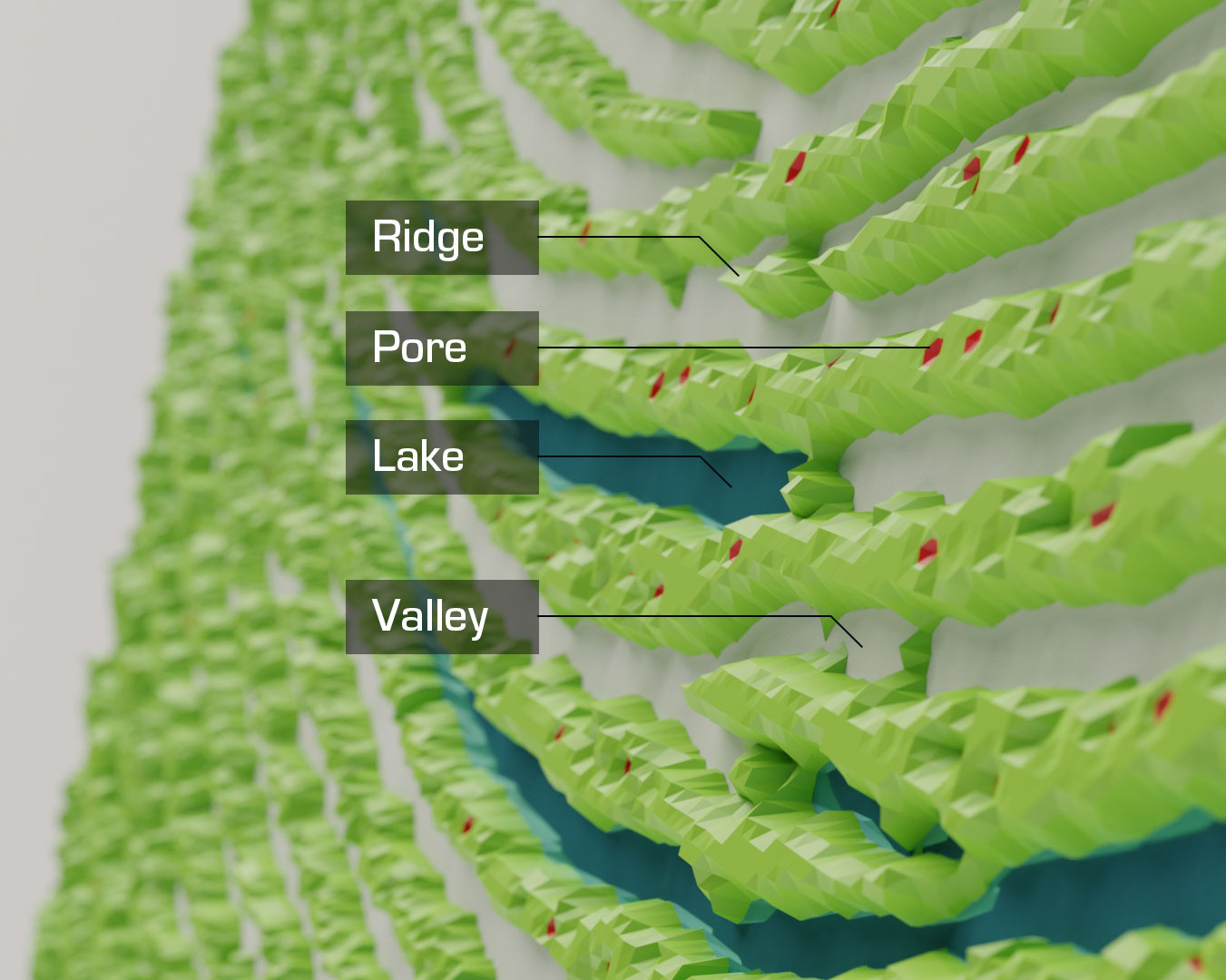
3D depth information reflects the overall structure of the human finger
- Distinctive 3D shape ridge features
- Valleys – length and depth
- Lakes/pores – location and depth
3D applied
From the medical field to the licensing office, 3D fingerprinting can be applied in any industry or exercise that relies on fingerprinting to improve security, increase efficiency, or enhance convenience, including the following:
- Law enforcement
- Background checks
- Surveillance
- Border control
- Fraud reduction
- Trusted traveler
- Physical access control
- Time and attendance
- Consumer recognition
- Remote authentication
- Asset protection
- Logical access control
- Medical diagnostics